Quench Your Thirst for Sustainability: Exploring Eco-Friendly Drink Packaging
Consumers demand sustainable drink packaging. For beverage brands, it’s crucial for market competitiveness. This listicle presents eight innovative solutions for sustainable drink packaging, outlining their benefits and real-world applications. Discover how plant-based PLA bottles, aluminum cans with increased recycled content, paper-based bottles, refillable glass systems, biodegradable seaweed packaging, rPET bottles, molded fiber carriers, and reusable stainless steel containers can elevate your brand’s commitment to environmental responsibility. Let Theory House guide your brand in navigating the sustainable packaging market.
1. Plant-Based PLA (Polylactic Acid) Bottles
In the quest for sustainable drink packaging, plant-based PLA (Polylactic Acid) bottles have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics. PLA is a biodegradable plastic derived from renewable resources, primarily corn starch, but also cassava roots or sugarcane. Through a fermentation process, these plant starches are converted into lactic acid, which is then polymerized to create PLA. This process results in a material with similar physical properties to conventional plastics like PET, making it suitable for bottling beverages while offering significant environmental advantages. PLA offers a compelling solution for brands seeking to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and minimize their environmental impact.
PLA bottles boast several attractive features for sustainable drink packaging. They are transparent, allowing for product visibility, and are suitable for containing cold beverages. A key advantage of PLA is its biodegradability in industrial composting facilities, where it can break down in 3-6 months, unlike conventional plastics that persist in the environment for centuries. This biodegradability contributes to a significantly lower carbon footprint, up to 80% lower than petroleum-based alternatives. Furthermore, PLA is non-toxic when incinerated, offering a safer disposal option compared to some traditional plastics.
Pros:
- Renewable Source Material: Reduces reliance on finite fossil fuels and supports sustainable agriculture.
- Biodegradable: Breaks down in industrial composting facilities within 3-6 months.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional plastics.
- Aesthetically Similar to Conventional Plastic: Offers clarity and a familiar look and feel for consumers.
- Non-toxic Incineration: A safer alternative if incineration is the chosen disposal method.
Cons:
- Requires Industrial Composting: Will not biodegrade in home composting environments or landfills. Limited industrial composting infrastructure poses a challenge in many regions.
- Not Suitable for Hot Beverages: PLA has low heat resistance, limiting its use to cold drinks.
- Higher Cost: Currently more expensive than conventional plastic bottles.
- Contamination Risk: Can contaminate PET recycling streams if improperly disposed of.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Danone: Utilizes PLA for Volvic and evian water bottles in select markets.
- JUST Water: Incorporates PLA in a portion of their paper-based bottle caps.
- Noble Juice: Packages refrigerated juices in PLA bottles.
- Biota Spring Water: Employs PLA for their water bottle packaging.
Tips for Implementation:
- Clear Labeling: Label bottles clearly as “PLA” to prevent contamination of PET recycling streams.
- Target Cold Beverages: Focus on using PLA for cold beverages and refrigerated products.
- Composting Partnerships: Collaborate with industrial composting facilities in your market to ensure proper disposal.
- Consumer Education: Educate consumers about the importance of proper disposal and the availability of composting facilities.
Popularized By:
- NatureWorks: Leading manufacturer of Ingeo PLA.
- Total Corbion PLA: Major PLA producer.
PLA bottles represent a significant step towards more sustainable drink packaging. While challenges remain regarding cost and end-of-life infrastructure, the benefits of using renewable resources, reducing carbon footprint, and promoting biodegradability make PLA a strong contender in the move away from traditional plastics. For brands committed to environmental responsibility and seeking a tangible way to reduce their impact, exploring PLA bottle options is a crucial step.
2. Aluminum Cans with Increased Recycled Content
In the quest for sustainable drink packaging, aluminum cans with increased recycled content are emerging as a frontrunner. Aluminum is inherently circular, meaning it can be recycled endlessly without losing its quality. This makes it a compelling choice for beverage brands seeking eco-friendly solutions that resonate with environmentally conscious consumers. Companies are now actively increasing the percentage of recycled aluminum in their cans, further minimizing their environmental footprint and contributing to a closed-loop system. This approach aligns with the growing demand for sustainable practices and offers a viable pathway towards a more circular economy within the beverage industry.

Aluminum’s infinite recyclability is a key differentiator in the sustainable packaging landscape. Unlike some materials that degrade with each recycling cycle, aluminum retains its strength and integrity, allowing it to be repurposed repeatedly. This significantly reduces the need for virgin aluminum production, which is an energy-intensive process. In fact, using recycled aluminum saves approximately 95% of the energy required to produce new aluminum from bauxite ore. Furthermore, aluminum cans are lightweight yet strong, providing excellent barrier properties against light, oxygen, and moisture, ensuring product freshness and extending shelf life. Their quick cooling properties are also a significant advantage for beverages.
The benefits of using aluminum with increased recycled content are numerous. The possibility of a closed-loop recycling system minimizes waste and resource depletion. The significantly lower energy consumption during recycling reduces greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to a smaller carbon footprint overall. The high recycling rates of aluminum (currently around 75% of all aluminum ever produced is still in use) demonstrate the practicality and effectiveness of this material in a circular economy. The lightweight nature of aluminum cans also translates to lower transportation emissions compared to heavier packaging alternatives like glass.
However, there are some considerations to keep in mind. The initial production of aluminum, even with recycled content, has a higher carbon footprint compared to some alternatives. The energy-intensive smelting process required for primary aluminum production remains a challenge. The internal coating of cans, typically epoxy-based, can contain BPA or similar chemicals, raising potential health concerns although BPA-free alternatives are becoming more readily available. Finally, aluminum can contaminate other recycling streams if not properly sorted.
Several companies are leading the charge in adopting aluminum cans with increased recycled content. Ball Corporation, a leading can manufacturer, is championing aluminum cups as sustainable alternatives to plastic. Coca-Cola has transitioned Dasani water to aluminum cans. Corona has pioneered aluminum-based multi-pack holders, eliminating plastic rings. Brew Dr. Kombucha has also made the switch from glass to aluminum, demonstrating its versatility across beverage categories. Even personal care brands like Every Man Jack are adopting aluminum for their packaging.
For brands seeking to maximize the sustainability of their drink packaging, several actionable steps can be taken. Sourcing cans with the highest possible recycled content is crucial. Opting for internal coatings that are BPA-free mitigates potential health risks. Educating consumers about the recyclability of aluminum and the importance of proper disposal reinforces the closed-loop system. Finally, designing cans for minimal material use without compromising their strength further optimizes resource efficiency. By embracing these strategies, beverage companies can leverage the significant advantages of aluminum and contribute to a more sustainable future for the industry.
3. Paper-based Bottles
Paper-based bottles represent a significant advancement in sustainable drink packaging, offering a compelling alternative to traditional plastic bottles. These innovative containers utilize molded paper pulp or paperboard as the primary structural component, typically incorporating a thin inner liner to ensure liquid containment. This approach drastically reduces plastic usage while capitalizing on the renewable and biodegradable properties of paper fibers, making it a key player in the quest for more eco-friendly packaging solutions. Paper-based bottles contribute to a lower carbon footprint and communicate a strong visual message of sustainability to environmentally conscious consumers.
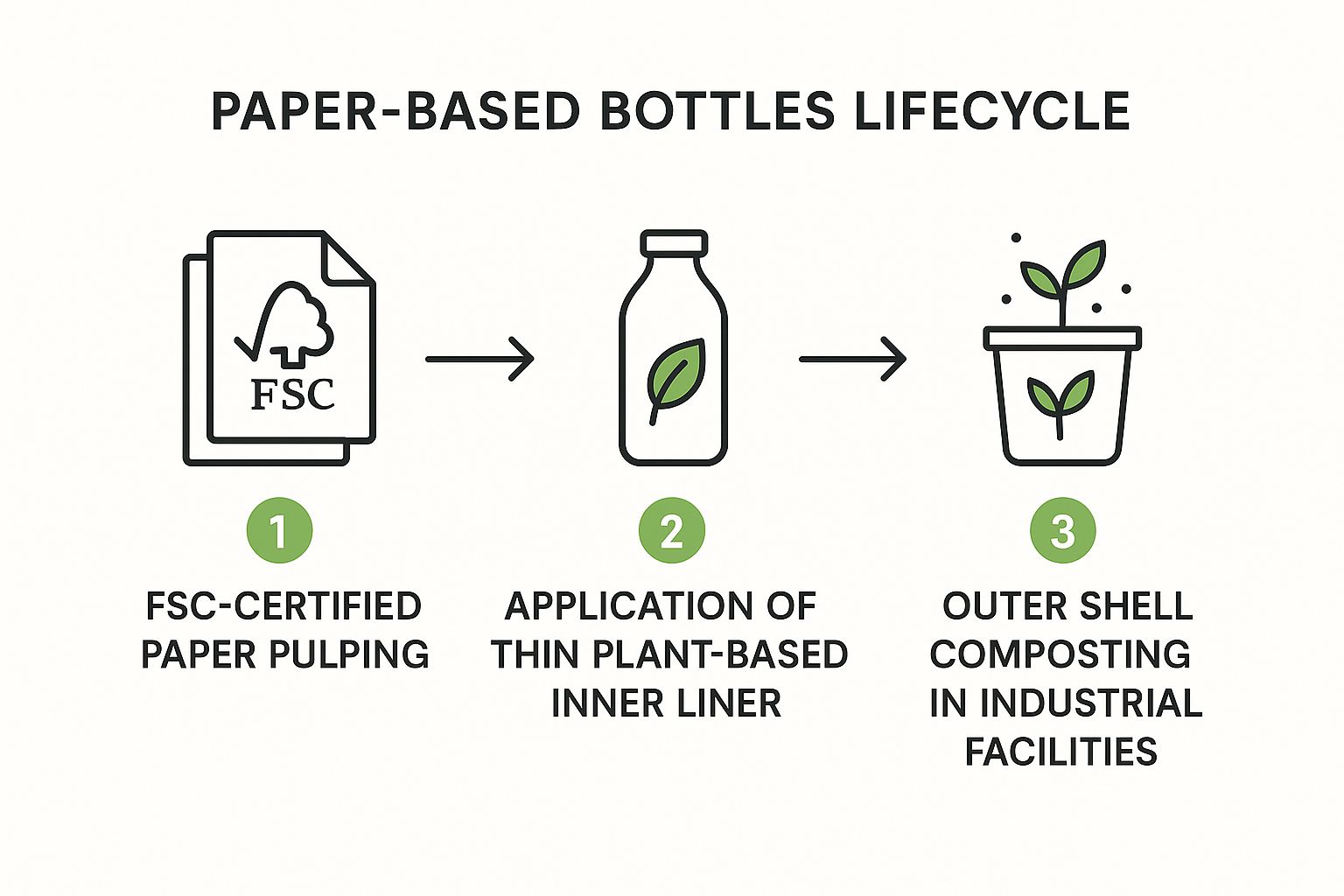
The infographic above visualizes the typical process flow for creating a paper-based bottle. The process begins with sourcing sustainable fiber materials, which are then pulped and molded into the desired bottle shape. Next, a barrier coating is applied to the inner surface to ensure liquid compatibility and prevent leakage. Finally, the bottle is cured, labeled, and filled, ready for distribution. The key takeaway from this visualization is the emphasis on sustainable materials and processes throughout the lifecycle of the paper-based bottle, from responsible sourcing to the potential for biodegradability at the end of its use.
Several companies have successfully implemented paper-based bottle technology. Carlsberg’s Green Fiber Bottle initiative, Diageo’s Johnnie Walker paper-based bottles, and Frugalpac’s Frugal Bottle for wines and spirits demonstrate the viability of this packaging format across different beverage categories. Paboco (Paper Bottle Company), a joint venture between BillerudKorsnäs and ALPLA, has also been instrumental in driving innovation and collaborating with major brands like Coca-Cola, Absolut, and L’Oréal on paper-based packaging solutions.
Features and Benefits:
- Sustainable Materials: Primarily made from FSC-certified paper or other sustainable fiber sources.
- Reduced Plastic: Significantly less plastic content compared to conventional bottles, though a thin inner barrier layer is often necessary.
- Customizable: Offers flexibility in bottle shapes and readily accepts printing for branding.
- Biodegradable Outer Shell: The paper component is biodegradable, contributing to a reduced environmental impact.
- Lightweight: Reduces transportation emissions due to lower weight compared to glass or some plastic bottles.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Renewable and sustainable forestry resources.
- Lower carbon footprint than plastic equivalents.
- Biodegradable outer shell (paper component).
- Communicates sustainability visually to consumers.
- Lightweight, reducing transportation emissions.
Cons:
- Often contains some plastic components (though significantly reduced).
- Higher production costs than conventional packaging.
- Still-developing technology with limited scalability.
- Mixed materials can complicate recycling.
- Water resistance and shelf life can present challenges depending on the product and barrier technology.
When and Why to Use Paper-Based Bottles:
Paper-based bottles are ideal for brands committed to sustainable packaging and seeking to reduce their reliance on plastic. They are particularly suitable for beverages with shorter shelf-life requirements, and for brands targeting environmentally conscious consumers. As the technology continues to develop, expect to see wider adoption across various beverage categories.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Clear Disposal Instructions: Clearly communicate disposal instructions to consumers for proper separation and recycling of different material components.
- Shelf-Life Considerations: Consider product shelf-life requirements when selecting barrier technologies to ensure product integrity.
- Early Supplier Partnerships: Partner with material suppliers early in the development process to ensure access to sustainable and compatible materials.
- Optimized Design: Optimize bottle designs for efficient stacking and transportation to minimize logistical costs and environmental impact.
- FSC Certification: Pursue FSC certification for paper materials to demonstrate commitment to responsible forestry practices.
Paper-based bottles deserve their place on this list due to their potential to revolutionize sustainable drink packaging. By leveraging renewable resources, minimizing plastic use, and offering a compelling visual narrative of environmental responsibility, these bottles address key concerns for both brands and consumers. While the technology is still evolving, the ongoing advancements and increasing adoption rates signify a promising future for paper-based bottles in the beverage industry.
4. Refillable Glass Systems
Refillable glass systems offer a closed-loop solution for sustainable drink packaging, significantly reducing waste and environmental impact. This system operates on a circular model: durable glass bottles are designed for repeated use, collected, thoroughly cleaned and sterilized, then refilled and redistributed. This cycle can repeat numerous times, drastically extending the lifespan of the packaging and minimizing the need for new bottle production. This makes refillable glass systems a highly attractive option for businesses seeking truly sustainable packaging solutions.

Refillable glass systems depend on several key features. Bottles are manufactured from thick-walled, durable glass specifically designed to withstand multiple washing and sterilization cycles. Standardized bottle designs are crucial for efficient collection, cleaning, and sorting processes. Deposit return schemes incentivize consumer participation by offering a refund upon bottle return. These systems often operate locally or regionally to minimize transport emissions and facilitate closed-loop operations, requiring specialized washing and sterilization facilities.
Pros:
- Significantly reduced carbon footprint: Studies show up to an 85% reduction in carbon emissions compared to single-use packaging.
- Waste elimination: Packaging waste is virtually eliminated for multiple use cycles.
- Material quality preservation: Glass doesn’t degrade between uses, ensuring consistent product quality.
- Job creation: Local jobs are created in collection, cleaning, and processing facilities.
- Proven technology: Refillable systems have a long history of successful implementation globally.
Cons:
- Higher initial production energy: Producing glass bottles requires more energy than producing single-use alternatives initially.
- Geographic limitations: Weight and transport emissions can restrict the geographic scope of these systems.
- Infrastructure requirements: Robust collection infrastructure is essential for success.
- Initial investment: Higher upfront investment is required for bottles and processing equipment.
- Consumer behavior change: Success hinges on consumer participation in returning bottles.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Germany’s mandatory refillable bottle system: Achieves an average of 22+ reuses per bottle.
- Oregon Beverage Recycling Cooperative: Operates a successful refillable beer bottle program.
- Ambev’s returnable beer bottle system (Brazil): A large-scale example of refillable systems in Latin America.
- Loop platform: Partners with major beverage brands to offer refillable options through a subscription service.
Tips for Implementation:
- Design for durability: Aim for bottles that can withstand 30+ washing cycles.
- Incentivize returns: Offer clear and attractive deposit refunds.
- Standardize bottle designs: Promote interoperability and efficiency across producers.
- Localize operations: Focus on local/regional implementation to minimize transport distance.
- Track bottle lifecycles: Utilize QR codes or other tracking technologies to monitor bottle usage and optimize the system.
Why Refillable Glass Systems Deserve a Place on this List: In the pursuit of truly sustainable drink packaging, refillable glass stands out as a proven and effective solution. It addresses key environmental concerns by significantly reducing carbon emissions and waste. While initial investment and logistical considerations exist, the long-term benefits for the planet and, ultimately, brand image, make refillable glass systems a crucial component of a comprehensive sustainable packaging strategy. For beverage companies, retailers, and spirits brands seeking a genuinely impactful solution, refillable glass presents a compelling and increasingly popular pathway towards a more circular and environmentally responsible future. This approach resonates with environmentally conscious consumers and positions brands as leaders in sustainability.
5. Biodegradable Seaweed-Based Packaging
As the demand for sustainable drink packaging intensifies, seaweed-based solutions are emerging as a promising alternative to conventional plastics. This innovative approach utilizes various species of algae to create flexible films, molded containers, and even edible coatings, offering a truly eco-friendly option for beverage brands. This makes seaweed-based packaging a crucial consideration for any brand director, marketing director, or CMO striving for genuine sustainability.
Seaweed-based packaging leverages the natural properties of algae. Different seaweed species are processed and combined to achieve specific textures and functionalities, from thin films suitable for sachets to rigid structures capable of holding liquids. The resulting material biodegrades naturally in both home and commercial composting environments, typically within 4-6 weeks, leaving no harmful microplastics behind. This rapid decomposition is a significant advantage over many bioplastics that require specialized industrial composting facilities.
Features and Benefits:
- Sustainably Sourced: Seaweed can be sustainably harvested from wild populations or cultivated in aquaculture farms, minimizing environmental impact. This resonates with consumers increasingly concerned about sourcing and its impact on oceans.
- Fully Biodegradable: Seaweed packaging breaks down completely and quickly, significantly reducing waste and pollution. This is a powerful selling point for eco-conscious consumers.
- Marine-Safe Degradation: Unlike many bioplastics which can persist in marine environments, seaweed packaging degrades harmlessly in the ocean, protecting marine ecosystems. This aligns with corporate social responsibility goals focused on ocean health.
- Carbon-Negative Production: Seaweed absorbs CO2 during its growth cycle, making its production carbon-negative and contributing to a lower carbon footprint for beverage brands. This addresses the growing demand for carbon-neutral or carbon-negative products.
- Versatile Applications: Seaweed packaging can be designed as clear films, flexible pouches, or rigid containers, catering to diverse beverage packaging needs. This adaptability allows for seamless integration into existing product lines.
Pros and Cons for Beverage Brands:
Pros:
- Strong sustainability narrative appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Potential for premium pricing due to unique and eco-friendly nature.
- Reduction in plastic waste and associated environmental impact.
- Positive brand image and differentiation in a competitive market.
Cons:
- Higher production costs compared to conventional plastics can impact profitability.
- Limited shelf life for some applications may restrict product suitability.
- Scaling of manufacturing capacity is still underway, potentially creating supply chain challenges.
- Taste and texture considerations for edible versions require careful product development.
- Limited heat resistance may preclude use with hot beverages.
Successful Implementations:
- Notpla’s Ooho: Edible water pouches made from seaweed, showcasing the potential for innovative and waste-free hydration solutions (used at the London Marathon).
- Just Eat’s seaweed-lined containers: Demonstrating the application of seaweed coatings to improve the sustainability of existing food and beverage packaging.
- Loliware’s seaweed-based straws: Offering a readily biodegradable and marine-safe alternative to plastic straws, addressing a specific and highly visible source of plastic pollution.
- Evoware’s seaweed-based sachets and wraps: Providing biodegradable packaging solutions for a range of food and beverage products.
Actionable Tips for Beverage Brands:
- Start Small: Begin with simple applications like sachets, straws, or liners for existing containers to test market acceptance and refine production processes.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Partner with established and reputable seaweed farms to ensure a sustainable supply chain.
- Educate Consumers: Clearly communicate the biodegradability benefits of seaweed packaging to consumers, highlighting its environmental advantages.
- Target Niche Markets: Focus on premium beverages or eco-conscious consumer segments where the added value of sustainable packaging is most appreciated.
- Collaborate with Experts: Partner with companies specializing in seaweed packaging technology to navigate the complexities of material selection, production, and application.
Seaweed-based packaging deserves its place on this list because it represents a genuine step towards a circular economy for the beverage industry. By addressing key environmental concerns related to plastic waste and carbon emissions, it offers a compelling and innovative solution for brands seeking to build a more sustainable future. While challenges remain in terms of scalability and cost, the potential of seaweed-based packaging is undeniable and warrants serious consideration by forward-thinking beverage companies.
6. rPET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate) Bottles
In the quest for sustainable drink packaging, rPET (recycled polyethylene terephthalate) bottles have emerged as a leading solution. This approach leverages post-consumer recycled PET plastic, the same material used in traditional PET bottles, to create new beverage containers. By utilizing existing plastic waste, rPET significantly reduces the need for virgin plastic production, lessening the environmental burden associated with extracting and processing fossil fuels. This “closed-loop” system makes rPET a cornerstone of sustainable packaging strategies for beverage companies seeking to minimize their impact.
rPET bottles function almost identically to their virgin PET counterparts, offering comparable performance in terms of durability, clarity, and barrier properties. They can be produced with varying levels of recycled content, ranging from 25% to 100%, offering flexibility for brands at different stages of their sustainability journey. Moreover, rPET bottles are compatible with existing recycling infrastructure, meaning consumers can easily recycle them within established municipal systems. They are also available in both transparent and colored options, allowing for brand consistency and visual appeal.
Features and Benefits:
- Material Source: Made from post-consumer recycled PET bottles.
- Recycled Content: Flexible integration of recycled material, from 25% to 100%.
- Performance: Similar properties to virgin PET, maintaining bottle integrity and product safety.
- Recyclability: Compatible with existing recycling infrastructure, promoting circularity.
- Aesthetics: Available in transparent or colored options, catering to diverse branding needs.
Pros:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Significantly reduces virgin plastic production and associated fossil fuel use, resulting in a 30-40% lower carbon footprint compared to virgin PET.
- Economic Benefits: Creates demand for recycled materials, supporting recycling economics and incentivizing further collection and processing.
- Consumer Familiarity: Similar in appearance and function to traditional PET, easing consumer adoption and requiring minimal changes to existing recycling habits.
- High Recyclability Rate: Fully recyclable in most municipal systems, further contributing to closed-loop sustainability.
Cons:
- End-of-Life Concerns: While recyclable, rPET is still a plastic product with potential end-of-life challenges if not properly managed within the recycling system.
- Supply Chain Limitations: Limited global supply of food-grade recycled PET can pose challenges for companies aiming for high recycled content targets.
- Cost Considerations: Slightly higher production costs compared to virgin PET, though this gap is narrowing as demand and supply increase.
- Quality Degradation: Potential for quality degradation after multiple recycling cycles, necessitating the introduction of some virgin material in many cases.
- Color and Additive Challenges: Certain colors and additives can complicate the recycling process and limit the usability of recycled material.
Successful Implementations:
Several major beverage companies have embraced rPET as a key component of their sustainable drink packaging strategies:
- evian: Has transitioned to 100% rPET bottles for its products in Europe.
- Coca-Cola: Is shifting to 100% rPET for certain brands in select markets as part of its “World Without Waste” initiative.
- PepsiCo: Converted its LIFEWTR brand to 100% rPET bottles.
- Nestlé Waters: Has committed to using 100% rPET across its major brands.
Actionable Tips for Beverage Brands:
- Design for Recyclability: Avoid problematic labels, adhesives, and colors that can hinder the recycling process.
- Secure Supply: Establish long-term supply contracts for high-quality, food-grade rPET to ensure consistent availability.
- Closed-Loop Systems: Explore and invest in bottle-to-bottle closed-loop systems to maximize resource efficiency.
- Transparent Communication: Clearly communicate recycled content percentages to consumers, showcasing your brand’s commitment to sustainability.
- Infrastructure Investment: Support and invest in recycling infrastructure development to ensure a steady supply of recycled materials.
When and Why to Use rPET:
rPET is an ideal solution for beverage brands seeking to improve the sustainability of their packaging. It offers a tangible way to reduce reliance on virgin plastic, lower carbon footprint, and support a circular economy. This approach is particularly relevant for companies targeting environmentally conscious consumers and aiming to meet growing regulatory pressures regarding plastic waste. For brand directors, marketing directors, and CMOs, adopting rPET demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility and can enhance brand reputation. By integrating rPET into your sustainable drink packaging strategy, you contribute to a healthier planet while also meeting consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
7. Molded Fiber Drink Carriers: A Sustainable Solution for Multi-Packs
Molded fiber drink carriers are emerging as a leading sustainable drink packaging solution, offering a robust alternative to traditional plastic multi-pack rings and shrink wraps. These carriers are crafted from recycled paper, sugarcane bagasse (a byproduct of sugar production), or other plant-based fibers, providing the necessary structural integrity to securely bundle beverage containers while significantly reducing plastic waste. This eco-friendly approach addresses growing consumer demand for sustainable options and helps beverage companies minimize their environmental impact.
How They Work: Molded fiber carriers utilize a pulping and molding process. The chosen fiber material is mixed with water and formed into a pulp. This pulp is then pressed into a mold, shaping the carrier to securely hold a specific number of beverage containers (typically four, six, or eight). Once dried, the carriers are ready for use.
Why Molded Fiber Carriers Deserve a Place on the List: Their inclusion in this list of sustainable drink packaging solutions is warranted due to their significant environmental benefits, brand-enhancing potential, and increasing viability as a practical alternative to plastic. They address a major source of plastic pollution – the ubiquitous plastic rings – while offering a compelling narrative around sustainability.
Features and Benefits:
- Material Source: Primarily made from recycled paper pulp or agricultural waste fibers, diverting these materials from landfills.
- Structural Integrity: Sturdy design that securely holds multiple containers, ensuring safe transport.
- Customization: Molds can be customized to accommodate various container shapes and sizes, offering flexibility for different product lines.
- Biodegradability and Compostability: Breaks down naturally in industrial composting facilities and sometimes even in home composting environments, reducing long-term waste.
- Branding Opportunity: Printable surfaces allow for branding and sustainability messaging, enhancing brand image and consumer appeal.
- 360-Degree Protection: Offers superior protection compared to plastic rings, minimizing damage during transport and handling.
Pros:
- Eliminates Plastic Rings: Directly addresses the issue of plastic rings that endanger marine life and contribute to plastic pollution.
- Compostable: Offers an end-of-life solution that avoids landfills and returns valuable nutrients to the soil.
- Utilizes Recycled and Waste Materials: Diverts waste streams and promotes circular economy principles.
- Strong Marketing Opportunity: Aligns with consumer values and strengthens brand image through demonstrable sustainability efforts.
- Enhanced Product Protection: Provides superior protection for containers compared to plastic rings.
Cons:
- Higher Material Cost: Currently more expensive than plastic alternatives, although costs are decreasing with increasing production and economies of scale.
- Bulkier than Plastic: Requires more storage space and can increase shipping costs.
- Moisture Resistance: While improving with ongoing innovations, molded fiber is generally less moisture-resistant than plastic. This requires careful consideration of the distribution chain and potential exposure to moisture.
- Equipment Requirements: May necessitate new equipment or modifications to existing packaging lines.
- Potentially Higher Shipping Emissions: Heavier weight compared to plastic can lead to increased transportation emissions if not offset by other logistical efficiencies.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Corona: Replaced plastic rings with fiber-based carriers, demonstrating a commitment to ocean conservation.
- Carlsberg: Introduced the “Snap Pack” and fiber-based carriers, reducing plastic usage in multi-packs.
- Heineken: Developed the “Green Grip” carriers made from recycled cardboard.
- Guinness: Switched to biodegradable cardboard carriers, further illustrating the trend towards sustainable packaging in the beverage industry.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Design Optimization: Design carriers for minimal material usage while maintaining the required strength and functionality.
- Moisture Management: Consider potential moisture exposure throughout the distribution chain and explore water-resistant coatings or treatments.
- Recycled Content: Prioritize the use of post-consumer recycled content to maximize environmental benefits.
- Production Line Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with existing or planned high-speed production lines to avoid bottlenecks.
- Thorough Testing: Test carriers in various environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) before full-scale deployment to ensure performance and durability.
When and Why to Use This Approach: Molded fiber drink carriers are ideal for beverage companies seeking a sustainable alternative to plastic multi-pack solutions. This approach is particularly relevant for brands targeting environmentally conscious consumers and aiming to reduce their plastic footprint. While the higher initial cost and bulkier nature pose challenges, the long-term environmental benefits, combined with the positive brand impact, make molded fiber carriers a compelling choice for forward-thinking beverage companies.
Popularized By: Companies like E6PR (Eco Six Pack Ring), WestRock, Graphic Packaging International, and Stora Enso have been instrumental in developing and popularizing molded fiber drink carrier technology. While individual company websites can be researched, focusing on those providers relevant to your specific geographic location and production needs is recommended.
8. Reusable Stainless Steel Containers
For businesses seeking a truly sustainable drink packaging solution that aligns with premium brand positioning, reusable stainless steel containers represent a compelling option. These containers offer a durable, long-lasting alternative to single-use packaging, playing a significant role in reducing waste within the beverage industry and contributing to a circular economy model. This approach requires an upfront investment but offers long-term benefits for both the environment and brand image. They deserve a prominent place on this list due to their longevity, recyclability, and potential to drastically reduce reliance on single-use materials. This makes them a powerful tool in achieving sustainable drink packaging goals.
How They Work: Reusable stainless steel containers are designed for repeated refills, typically made from food-grade stainless steel (18/8 or 304 grade) known for its durability and corrosion resistance. Many models feature double-wall vacuum insulation, which allows them to maintain the temperature of both hot and cold beverages for extended periods. This insulation is a key differentiator from single-use alternatives and adds value for the consumer.
Features and Benefits:
- Durability: A lifespan of 10+ years significantly reduces the need for replacements, minimizing the environmental impact compared to disposable packaging.
- Temperature Retention: Vacuum insulation keeps drinks at their ideal temperature for hours, enhancing the consumer experience.
- Material Safety: Stainless steel is non-leaching and non-reactive with beverages, ensuring product quality and safety.
- Recyclability: At the end of their long life, these containers are fully recyclable, contributing to a closed-loop system.
- Branding Opportunity: High-quality, reusable containers offer a premium brand positioning opportunity and can foster brand loyalty.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Virtually eliminates packaging waste through multiple reuses.
- Excellent temperature retention properties.
- No chemical leaching concerns, unlike some plastics.
- Fully recyclable at end of life.
- Premium brand positioning opportunity.
Cons:
- Higher upfront cost to consumer or business.
- Heavier than single-use alternatives (transportation considerations).
- Requires consumer behavior change and cleaning between uses.
- Higher embodied energy in initial production.
- Potential for loss in deposit-return or refill systems.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Starbucks’ reusable cup program: Offers discounts to customers who bring their own reusable cups.
- MiiR’s partnerships with craft breweries: Provides co-branded reusable growlers and cups.
- S’well’s collaborations with beverage brands: Offers co-branded, designer stainless steel bottles.
- Klean Kanteen’s partnerships with outdoor events and festivals: Promotes reusable containers in eco-conscious settings.
- Loop (TerraCycle’s reuse platform): Partners with major brands to implement reusable packaging systems for various products, including beverages.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Implement deposit return systems: Incentivize container return and minimize loss.
- Create attractive designs: Encourage consumers to adopt and reuse the containers.
- Provide convenient cleaning stations: Facilitate easy cleaning in refill scenarios.
- Consider laser etching rather than adhesive labels: Ensure branding longevity and avoid peeling.
- Design systems that make reuse as convenient as single-use: Address the behavioral challenges associated with reusable systems. This might involve strategically placed refill stations, integrated app-based tracking, or other innovative solutions.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Reusable stainless steel containers are an ideal sustainable drink packaging solution for brands committed to reducing their environmental footprint and appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. This approach is particularly well-suited for:
- Premium beverage brands: Reinforces brand image and aligns with consumer values.
- On-the-go consumption: Durable and portable, perfect for active lifestyles.
- Businesses with established refill infrastructure: Maximizes the benefits of reusable systems.
- Companies seeking long-term sustainability solutions: Reduces reliance on single-use packaging and minimizes waste.
By investing in reusable stainless steel container programs, beverage companies can demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, enhance brand perception, and contribute to a more circular economy. The initial investment is offset by long-term cost savings from reduced packaging purchases and the positive impact on brand reputation.
Sustainable Drink Packaging: 8-Material Comparison
| Packaging Concept / Material | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements 💡 | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based PLA (Polylactic Acid) Bottles | Moderate 🔄 | Requires industrial composting infrastructure | Biodegradable in industrial composting; lower carbon footprint 📊 | Cold beverages & refrigerated products | Renewable, biodegradable, similar look to PET ⭐ |
| Aluminum Cans with Increased Recycled Content | Moderate-High 🔄 | High energy in primary production, recycled content sourcing | High recyclability; strong barrier; reduced transport emissions 📊 | Wide beverage packaging requiring protection | Infinitely recyclable; lightweight; strong barrier ⭐ |
| Paper-based Bottles | High 🔄 | Sustainable fiber sourcing; thin inner barrier materials | Reduced plastic use; biodegradable outer shell; emerging scalability 📊 | Sustainable premium beverage packaging | Renewable materials; biodegradable outer shell; visual sustainability ⭐ |
| Refillable Glass Systems | High 🔄 | Durable glass production; washing & sterilization infrastructure | Up to 85% CO2 reduction with reuse; circular lifecycle 📊 | Local or regional reuse-focused beverage systems | Multiple reuse cycles; waste elimination; proven technology ⭐ |
| Biodegradable Seaweed-Based Packaging | Moderate 🔄 | Sustainable seaweed farming; emerging production | Rapid biodegradation; carbon negative production 📊 | Short shelf-life products; food service sachets, straws | Marine-safe degradation; edible options; carbon negative ⭐ |
| rPET (Recycled PET) Bottles | Moderate 🔄 | Reliable supply of food-grade recycled PET | Reduced virgin plastic demand; recyclable in existing systems 📊 | Standard beverages moving toward circularity | Reduces fossil fuel use; familiar performance; recyclable ⭐ |
| Molded Fiber Drink Carriers | Low-Moderate 🔄 | Recycled/agricultural fiber sourcing | Eliminates plastic multipack waste; compostable end-of-life 📊 | Multi-pack beverage bundling | Compostable; sustainable alternative to plastic rings ⭐ |
| Reusable Stainless Steel Containers | High 🔄 | High-quality stainless steel and insulation tech | Long lifespan; drastically reduced packaging waste 📊 | Premium reusable beverage containers; hot/cold drinks | Durable; excellent insulation; recyclable; multiple reuse ⭐ |
The Future of Refreshment: Sustainable Sips for a Healthier Planet
From plant-based PLA bottles to innovative seaweed-based packaging, the future of sustainable drink packaging is brimming with exciting possibilities. This article has explored a range of eco-friendly alternatives, including aluminum cans with increased recycled content, paper-based bottles, refillable glass systems, rPET bottles, molded fiber carriers, and even reusable stainless steel containers. Mastering the application of these sustainable drink packaging solutions is crucial for any beverage brand aiming to minimize its environmental footprint and meet growing consumer demand for responsible practices. These shifts not only benefit the planet by reducing waste and reliance on fossil fuels but also enhance brand image and resonate with environmentally conscious consumers. Beyond beverages, considering the environmental impact of all packaging is crucial. For brands looking to minimize their environmental impact across their product line, exploring eco-friendly disposable food containers is a crucial step, as outlined in this helpful resource from MrTakeOutBags.com.
The shift towards sustainable drink packaging is more than a trend; it’s a necessary evolution. By embracing innovation and prioritizing eco-conscious choices, the beverage industry can significantly contribute to a healthier planet, one sip at a time. Ready to elevate your brand with sustainable packaging solutions that resonate with consumers and protect the environment? Partner with Theory House to explore how our expertise in branding and packaging can help you implement impactful and innovative sustainable drink packaging strategies.




