Connecting Every Touchpoint: Why Omnichannel Matters Now
Today’s customers demand consistent experiences whether they interact online, via mobile, or in your physical locations. Fragmented marketing no longer works. Real growth, particularly for food, beverage, and CPG brands, requires mastering the entire customer journey. This listicle provides 7 essential omnichannel marketing strategies to help you unify digital and physical touchpoints. You will learn practical approaches including Customer Journey Mapping, Unified Customer Data Platforms (CDPs), Personalized Content Orchestration, Integrated Loyalty Programs, BOPIS and Omnichannel Fulfillment, Unified Messaging, and Cross-Channel Analytics. Implementing these omnichannel marketing strategies is key to fostering deeper customer connections and boosting sales significantly in 2025.
1. Customer Journey Mapping
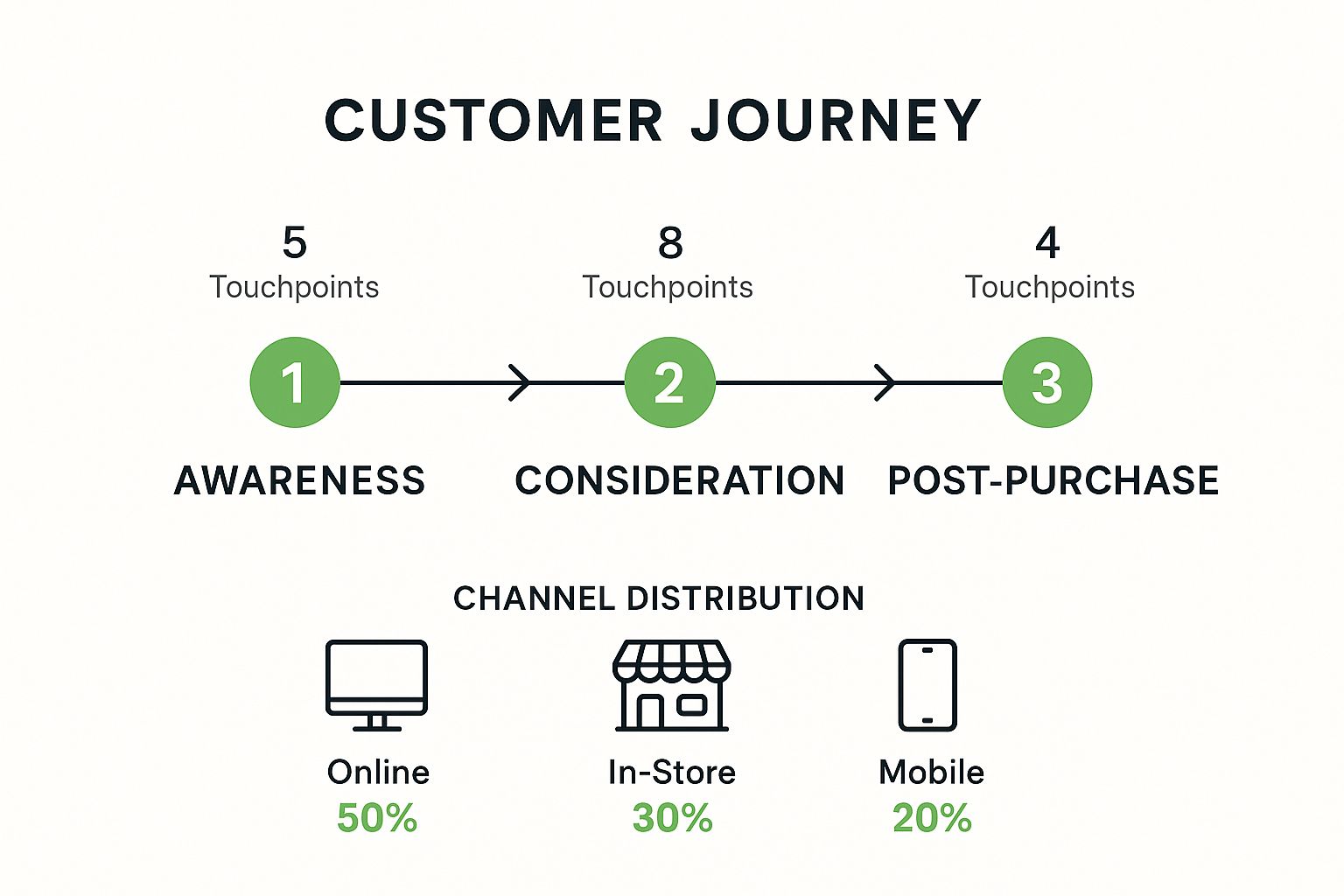
Customer Journey Mapping stands as a foundational element within effective omnichannel marketing strategies. It’s the process of creating a visual representation of the entire experience a customer has with your brand, spanning all potential channels and touchpoints. From the moment they first become aware of your product or service, through the consideration and purchase phases, and into post-purchase engagement and support, this map charts their interactions, thoughts, and emotions. By meticulously documenting this path, businesses gain invaluable insights into how customers actually experience their brand, moving beyond internal assumptions or siloed departmental views. This comprehensive understanding is critical for designing and delivering the seamless, consistent experiences that define successful omnichannel execution, making it a vital first step for any brand serious about unifying its customer interactions.
The following infographic illustrates the typical process flow involved in creating and utilizing a customer journey map, highlighting the key stages from initial research to ongoing optimization.
As visualized in the process flow, customer journey mapping typically begins with thorough research and persona definition, progresses through mapping the distinct stages and touchpoints, identifies friction points and emotional shifts, and culminates in actionable insights for improvement, forming a continuous cycle of refinement.
How it Works:
The core of customer journey mapping involves gathering data from various sources – website analytics, CRM data, social media listening, customer surveys, interviews, and front-line staff feedback. This data informs the creation of specific customer personas, representing key segments of your audience. For each persona, the journey is mapped chronologically, detailing:
- Stages: Key phases like Awareness, Consideration, Purchase, Retention, Advocacy.
- Touchpoints: Specific interaction points within each stage (e.g., seeing a social media ad, visiting a product page, using a mobile app, calling support, visiting a retail store).
- Actions: What the customer is doing at each touchpoint.
- Thoughts & Emotions: What the customer might be thinking or feeling (e.g., confused, excited, frustrated).
- Pain Points: Obstacles or frustrations encountered.
- Opportunities: Areas where the experience can be enhanced or made more seamless across channels.
Features and Benefits:
Customer Journey Mapping offers distinct advantages for developing robust omnichannel marketing strategies:
- Holistic Customer View: Provides a comprehensive understanding of the end-to-end customer experience, breaking down internal silos.
- Gap & Inconsistency Identification: Crucially highlights where disconnects occur between different channels (e.g., conflicting information online vs. in-store, lack of data sharing between sales and support). This is vital for omnichannel success.
- Prioritization of Investments: Helps businesses focus resources on the moments and touchpoints that matter most to customers or cause the most friction.
- Enhanced Customer-Centricity: Embeds a deep understanding of customer needs, motivations, and emotions into marketing and operational decisions.
- Improved Cross-Functional Alignment: The process itself necessitates collaboration between marketing, sales, product development, and customer service, fostering a unified approach.
When and Why Use This Approach?
Employ customer journey mapping when:
- You suspect inconsistencies in the customer experience across channels.
- Customer satisfaction scores are declining, or churn rates are increasing.
- You are launching new products, services, or channels and want to ensure a smooth integration.
- You need to gain buy-in and alignment across different departments for customer-centric initiatives.
- You aim to move from a channel-specific approach to a truly integrated omnichannel strategy.
It deserves its place at the forefront of omnichannel marketing strategies because you cannot optimize or integrate journeys you don’t fully understand. It provides the diagnostic map needed before prescribing solutions.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Sephora: Their renowned Beauty Insider program is underpinned by journey mapping, seamlessly connecting online browsing history and wishlists with personalized in-store consultations and targeted post-purchase email engagement, creating a unified experience regardless of the channel used.
- Bank of America: Faced with disjointed experiences between their mobile app, online banking portal, and physical branches, BofA used journey mapping to identify key friction points. This led to a redesign that streamlined common tasks and ensured greater consistency across platforms.
- Starbucks: The development of their highly successful mobile order and pay system was heavily influenced by journey mapping. They analyzed the existing customer journey, identified bottlenecks (like waiting in line), and designed a digital solution that integrates flawlessly with the physical store experience, enhancing convenience and efficiency.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Develop Persona-Specific Maps: Don’t try to create a single map for everyone; tailor maps to distinct customer segments or personas.
- Use Real Data: Ground your maps in qualitative and quantitative customer data, not just internal assumptions.
- Include Emotions: Map customer feelings (frustration, delight, confusion) at each stage to identify critical moments.
- Involve Cross-Functional Teams: Bring together representatives from marketing, sales, service, IT, and operations for a richer, more accurate map.
- Review and Update Regularly: Customer behaviors and channel landscapes evolve. Review and update your maps at least quarterly or biannually.
- Focus on Omnichannel Linkages: Pay special attention to transitions between channels – are they smooth or jarring?
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Holistic view, identification of gaps/inconsistencies, aids investment prioritization, increases customer focus.
- Cons: Can be resource-intensive (time, personnel), requires strong cross-departmental collaboration and buy-in, may risk oversimplifying complex behaviors if not done well, needs ongoing maintenance.
While resource-intensive, the insights gained from thorough Customer Journey Mapping are invaluable for diagnosing experience flaws and strategically designing the truly seamless interactions required by today’s omnichannel customer. It provides the essential foundation upon which other sophisticated omnichannel marketing strategies can be built.
2. Unified Customer Data Platforms (CDPs)
Why This Matters for Omnichannel Success: In today’s fragmented digital and physical landscape, customers interact with your brand across numerous touchpoints – your website, mobile app, social media, email, physical stores, customer service calls, and more. Without a way to connect these interactions, your understanding of the customer is incomplete, leading to disjointed experiences and missed opportunities. Unified Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are foundational technology for executing sophisticated omnichannel marketing strategies precisely because they solve this fragmentation problem, creating a single, reliable source of truth for all customer data. For Brand Directors, Marketing Directors, and CMOs, particularly in competitive sectors like beverage, retail, and spirits, a CDP is often the key to unlocking true personalization at scale and driving measurable results.
What is a CDP and How Does it Work?
A Customer Data Platform is a type of software that aggregates and organizes customer data from all available sources to build a single, coherent, and comprehensive view of each individual customer. Think of it as the central nervous system for your customer intelligence.
Here’s a breakdown of how it typically functions:
- Data Ingestion: CDPs collect data in real-time (or near real-time) from a wide array of sources. This includes:
- Behavioral Data: Website clicks, page views, app usage, video views, email opens/clicks.
- Transactional Data: Online purchases, in-store POS transactions, returns, subscription status.
- Demographic Data: Name, address, email, phone number, age (often from CRM or sign-up forms).
- CRM Data: Customer service interactions, sales history, loyalty program status.
- Offline Data: Data from events, direct mail responses (if digitized), in-store interactions logged by associates.
- Third-Party Data (Optional): While primarily focused on first-party data, some CDPs can integrate second or third-party data for enrichment, though this requires careful privacy considerations.
- Identity Resolution: This is a critical function. The CDP uses sophisticated algorithms and rules to stitch together data points from different sources belonging to the same individual, even across different devices or identifiers (e.g., linking a user’s cookie ID on the website to their email address from a purchase and their loyalty ID from an in-store visit). This creates a persistent, unified customer profile.
- Profile Unification & Enrichment: The collected and resolved data is organized into individual customer profiles, providing a 360-degree view. These profiles can be enriched with calculated attributes like lifetime value (LTV), churn risk, product affinities, or engagement scores.
- Segmentation & Audience Building: Marketing teams can use the CDP interface to easily create specific audience segments based on any combination of attributes, behaviors, or transactions stored in the unified profiles (e.g., “customers who bought Product X online in the last 30 days but haven’t visited the app” or “high-value loyalty members living in a specific region”).
- Data Activation: The unified profiles and audience segments are then pushed to various activation channels and marketing tools via API connections or built-in integrations. This allows you to deliver consistent and personalized messages across:
- Email Marketing Platforms
- Advertising Networks (Social, Search, Display)
- Website Personalization Engines
- Mobile Push Notification Services
- CRM Systems (for sales/service teams)
- Customer Support Tools
Key Features & Benefits:
Implementing a CDP offers significant advantages for executing effective omnichannel marketing strategies:
- Single Source of Truth: Eliminates data silos between departments (marketing, sales, service, e-commerce) ensuring everyone works from the same complete customer picture.
- Deep Personalization: Enables highly relevant and consistent personalization across all channels, adapting experiences based on the customer’s complete history and real-time behavior.
- Improved Marketing ROI: Better audience segmentation and targeting lead to more efficient ad spend, higher conversion rates, and increased customer lifetime value.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Customers receive seamless, relevant interactions regardless of the channel they use, reducing friction and building loyalty.
- Agility & Speed: Real-time data flows allow for immediate responses to customer actions, such as abandoned cart recovery emails or personalized offers triggered by app activity.
- First-Party Data Control & Compliance: CDPs centralize the management of valuable first-party data, making it easier to manage consent and comply with evolving data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Examples of Successful CDP Implementation:
- Starbucks: Leverages its CDP to unify data from its popular mobile app, loyalty program (Starbucks Rewards), website interactions, and in-store purchases. This allows them to deliver hyper-personalized offers (e.g., suggesting a favorite drink modification or offering a bonus star challenge based on past purchase behavior) seamlessly across the app and email, enhancing customer engagement and driving repeat visits.
- Kroger (via 84.51°): Their sophisticated data platform acts like a CDP, integrating massive amounts of loyalty card purchase data (both in-store and online) with digital engagement signals. This powers highly personalized promotions delivered through their app, website, email, and even targeted direct mail, effectively bridging the physical and digital retail divide.
- Sephora: Uses its CDP to connect online browsing behavior (products viewed, items added to cart or wishlist) with Beauty Insider loyalty program data and in-store purchase history. This enables personalized product recommendations online, targeted emails about relevant products, and empowers store associates with insights for better in-person consultations, creating a truly unified experience.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros:
- Creates a unified, reliable view of the customer.
- Enables consistent, sophisticated personalization across channels.
- Improves marketing ROI through precise targeting and segmentation.
- Breaks down data silos, fostering cross-departmental collaboration.
- Strengthens control over first-party data and aids privacy compliance.
- Cons:
- Can involve significant upfront investment in software and implementation.
- Requires ongoing technical resources for maintenance, integration, and optimization.
- Effectiveness is highly dependent on the quality and completeness of the source data (“garbage in, garbage out”).
- Integrating with complex legacy systems can be challenging and time-consuming.
- Marketing teams may require training to fully leverage the platform’s capabilities (potential learning curve).
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Define Clear Use Cases: Don’t try to boil the ocean. Start by identifying 2-3 specific, high-impact omnichannel use cases you want to enable (e.g., coordinated online/offline promotions, personalized onboarding journeys, cross-channel cart abandonment recovery). Build momentum from there.
- Prioritize Data Governance: Establish clear rules for data quality, privacy, consent management, and security before you start implementation. Ensure compliance with all relevant regulations from day one.
- Map Your Data Sources: Thoroughly inventory all potential customer data sources across your organization. Understand the format, frequency, and quality of data in each system.
- Focus on Data Quality: Implement processes to clean, standardize, and validate data before it enters the CDP. Inaccurate or inconsistent data will undermine the entire initiative.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: CDP selection and implementation is not just an IT or marketing project. Involve representatives from Marketing, IT, Data Science, Sales, Customer Service, and Legal/Compliance early and often.
- Plan for Change Management: Ensure your teams are trained and prepared to adopt new workflows and leverage the insights provided by the CDP.
When and Why to Use a CDP:
A CDP becomes particularly crucial when:
- Your customers engage with your brand across multiple channels (online, offline, mobile, etc.).
- You struggle with fragmented data and lack a single view of the customer.
- Your personalization efforts feel generic or inconsistent across touchpoints.
- You need to improve marketing efficiency and demonstrate ROI more clearly.
- You are prioritizing the collection and ethical use of first-party data.
- Navigating data privacy regulations is a key business requirement.
In essence, if your goal is to move beyond basic multichannel marketing towards truly integrated, customer-centric omnichannel marketing strategies, a CDP provides the essential data foundation to make it possible. Leading platforms like Segment (Twilio Segment), Adobe Experience Platform, Salesforce Customer 360 (formerly Salesforce CDP), Tealium AudienceStream, and Treasure Data are powering these capabilities for brands worldwide.
3. Personalized Content Orchestration
Personalized Content Orchestration stands as a cornerstone among advanced omnichannel marketing strategies. It moves beyond generic messaging by delivering highly tailored content experiences across multiple channels, meticulously aligned with individual customer data, stated preferences, observed behaviors, and real-time context. This strategy leverages the power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and marketing automation platforms to dynamically assemble and deliver content, ensuring customers receive messaging that is not only consistent in its core brand values but also uniquely adapted to the specific channel and their current stage in the customer journey. The ultimate goal is to create a seamless, relevant, and cohesive brand narrative, regardless of whether the customer interacts via email, a mobile app, the website, social media, or even in-store digital displays.

How Personalized Content Orchestration Works:
At its heart, this strategy relies on a unified customer profile that aggregates data from various touchpoints. This data—ranging from demographic details and purchase history to browsing behavior, app usage, and email engagement—feeds into AI-driven decision engines. These engines analyze the information to understand individual needs, predict future behavior, and determine the most relevant content and offers. Automation workflows then trigger the delivery of this personalized content through the most appropriate channel at the optimal time. For instance, a customer abandoning a cart on your website might receive a personalized email reminder with the specific product, followed by a targeted ad on social media showcasing related items, and perhaps even a special offer via push notification if they use your mobile app.
Why This Strategy Deserves Its Place:
In an era of information overload and heightened customer expectations, generic marketing falls flat. Personalized Content Orchestration is crucial because it addresses the core challenge of omnichannel: delivering a unified and relevant experience. It transforms disparate channel interactions into a continuous, evolving conversation with the customer. For Brand Directors and CMOs in competitive sectors like beverages, retail, and spirits, this capability is not just a nice-to-have; it’s essential for cutting through the noise, building deeper customer loyalty, and maximizing the ROI of marketing efforts across the entire ecosystem. It is a pivotal element in executing sophisticated omnichannel marketing strategies that drive tangible business results.
Key Features:
- Dynamic Content Generation and Adaptation: Content elements (text, images, offers, CTAs) are automatically customized for each individual and channel context in real-time.
- Cross-Channel Messaging Consistency: Ensures core brand messages and user-specific information (like loyalty status or recent interactions) are reflected accurately across all platforms.
- Behavioral and Contextual Triggers: Content delivery is often triggered by specific user actions (e.g., website visit, purchase, inactivity) or contextual factors (e.g., location, time of day, device).
- Content Sequencing based on Customer Journey Stage: Orchestrates a series of messages that guide the customer logically through awareness, consideration, purchase, loyalty, and advocacy stages.
- A/B and Multivariate Testing Capabilities: Allows marketers to continuously test different personalization variables (offers, visuals, timing) to optimize performance across channels.
Benefits (Pros):
- Significantly Increases Engagement and Conversion Rates: Relevance drives action. Tailored content resonates more deeply, leading to higher click-through rates, conversions, and order values.
- Creates More Relevant and Valued Customer Experiences: Customers feel understood and catered to, strengthening their connection with the brand.
- Reduces Message Fatigue and Content Waste: By delivering only relevant content, it avoids overwhelming customers with irrelevant information, improving reception and reducing opt-outs.
- Scales Personalization Across Multiple Touchpoints: AI and automation make it feasible to deliver individual-level personalization across a vast customer base and numerous channels.
- Supports Progressive Customer Relationship Building: Each interaction builds upon the last, creating a richer understanding of the customer and enabling increasingly sophisticated personalization over time.
Challenges (Cons):
- Requires Substantial Content Creation Resources: Dynamic content demands a modular approach and a larger volume of content assets to cover various personalization scenarios.
- Complex Implementation and Management: Integrating data sources, setting up automation rules, and managing cross-channel workflows can be technically demanding and require specialized expertise.
- Risks of Personalization Feeling Intrusive if Poorly Executed: Overly specific or inaccurate personalization can feel creepy or annoying, potentially damaging the customer relationship.
- Dependent on High-Quality, Unified Customer Data: The effectiveness hinges entirely on the accuracy, completeness, and accessibility of customer data across systems. Data silos are a major obstacle.
- Can Be Technically Challenging to Implement Across Legacy Channels: Integrating personalization into older systems or physical touchpoints (like POS or traditional media) can be difficult.
When and Why to Use Personalized Content Orchestration:
This approach is particularly valuable when:
- You operate in multiple channels: The core premise is coordinating across touchpoints.
- You have access to rich customer data: The strategy thrives on data to fuel personalization.
- Your customer journey is complex or non-linear: Orchestration helps guide customers through varied paths.
- You aim to build long-term customer relationships and loyalty: Personalization fosters deeper connections than generic campaigns.
- Maximizing conversion rates and customer lifetime value are key objectives: Relevance directly impacts these metrics.
- You operate in a competitive market: Personalized experiences can be a significant differentiator.
For beverage, retail, and spirits brands, this means tailoring offers based on past purchase preferences (e.g., specific wine varietals, clothing styles, spirit types), reminding customers about items viewed but not purchased, sending location-based promotions for nearby stores or events, or personalizing loyalty program communications across email, app, and web.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Netflix: Its recommendation engine provides personalized suggestions on your smart TV, mobile app, and web browser, seamlessly syncing your viewing history and preferences across all platforms.
- Amazon: Masterfully uses browsing history, purchase data, and wish lists to display consistent and relevant product recommendations across its website, mobile app, email campaigns, and even off-site ads.
- Spotify: Creates personalized playlists like “Discover Weekly” and “Release Radar” that are accessible and synced across all devices, integrating recommendations into the user’s core experience and facilitating social sharing.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Develop Modular Content: Create content assets (headlines, images, body copy, CTAs) that can be easily mixed and matched by the personalization engine for different scenarios and channels.
- Start with High-Impact Customer Segments: Don’t try to personalize everything for everyone at once. Begin with your most valuable customer segments or key journey stages where personalization can yield the biggest wins, then scale gradually.
- Use Progressive Profiling: Continuously gather customer data over time through interactions rather than asking for everything upfront. This builds richer profiles gradually and feels less intrusive.
- Establish Clear Content Governance: Define rules and guidelines for how personalization is applied across channels to ensure brand consistency and avoid conflicting messages.
- Implement Regular Testing and Optimization: Continuously use A/B and multivariate testing to validate the effectiveness of your personalization rules and identify opportunities for improvement. What works today might need refinement tomorrow.
Popularized By Platforms:
This strategy is often enabled by sophisticated marketing technology platforms such as Adobe Target, Optimizely (including the former Dynamic Yield), Salesforce Marketing Cloud (especially Interaction Studio/Personalization), and Movable Ink, among others specializing in personalization and cross-channel campaign management.
4. Integrated Loyalty Programs: Building Deeper Connections Across Channels
In the complex landscape of modern commerce, where customers interact with brands across myriad touchpoints, Integrated Loyalty Programs stand out as a powerful pillar within effective omnichannel marketing strategies. Moving far beyond simple punch cards or siloed points systems, these programs are sophisticated ecosystems designed to recognize, reward, and retain customers consistently, whether they engage online, via a mobile app, or within a physical store. They serve as a crucial bridge, unifying the customer experience and providing brands with invaluable first-party data.
What It Is & How It Works
An Integrated Loyalty Program is essentially a customer relationship strategy that uses a centralized system to track and reward customer interactions and purchases across all sales and engagement channels. When a customer signs up, they gain access to a unified profile where their activities – website visits, app usage, in-store purchases, social media engagement, email interactions – contribute towards rewards, status tiers, and personalized benefits.
The core mechanism involves:
- Unified Customer ID: Assigning a unique identifier to each member that is recognized across all platforms.
- Data Aggregation: Collecting interaction and transaction data from various touchpoints (POS systems, e-commerce platforms, apps, CRM) into a central customer data platform (CDP) or loyalty engine.
- Real-time Recognition & Reward: Instantly updating points, status, and available rewards as interactions occur, regardless of the channel.
- Cross-Channel Redemption: Allowing members to earn points online and seamlessly redeem them in-store, or vice-versa, often facilitated through mobile apps or digital wallets.
This seamless integration ensures customers feel recognized and valued consistently, reinforcing their connection to the brand no matter how they choose to interact.
Why This Strategy Deserves Its Place
Integrated Loyalty Programs are fundamental to successful omnichannel marketing strategies because they directly address key challenges: bridging channel gaps, fostering genuine loyalty beyond transactional discounts, and gathering consented first-party data in a privacy-conscious era. They transform the customer relationship from episodic transactions into an ongoing dialogue, encouraging repeat business and higher lifetime value. For Brand Directors and CMOs, particularly in competitive sectors like retail, beverage, and spirits, these programs offer a tangible way to differentiate the brand and cultivate advocates.
Key Features and Capabilities:
- Cross-Channel Reward Recognition and Redemption: Points earned online instantly reflect in-app and are redeemable in-store (and vice-versa).
- Mobile and Digital Wallet Integration: Loyalty cards, status, and rewards are easily accessible via smartphone apps or integrated into mobile wallets (like Apple Wallet or Google Pay) for frictionless in-store use.
- Real-time Point Accrual and Status Updates: Customers see immediate feedback on their actions, reinforcing desired behaviors.
- Tiered Membership Structures: Offering escalating benefits (e.g., Bronze, Silver, Gold) motivates increased engagement and spend to unlock higher levels of recognition and reward.
- Experiential and Partner-Based Rewards: Moving beyond discounts to offer exclusive access, early product releases, special events, or rewards through partnerships (e.g., airline miles, partner brand discounts).
- Gamification Elements: Incorporating challenges, badges, or surprise rewards to make engagement more interactive and fun.
Why and When to Use Integrated Loyalty Programs:
- To Increase Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) & Retention: Loyal members tend to purchase more frequently and spend more over time. These programs provide compelling reasons for customers to choose your brand repeatedly.
- To Gather Rich First-Party Data: Members willingly share data in exchange for value. This cross-channel data provides a holistic view of customer behavior, preferences, and journey, fueling hyper-personalization efforts across marketing channels.
- To Encourage Multichannel Engagement: By rewarding interactions across different touchpoints, brands can incentivize customers to explore and utilize various channels (e.g., download the app, visit a store, engage online).
- To Build Emotional Connections: Well-designed programs focusing on recognition, exclusivity, and experiences foster a deeper, emotional bond that transcends price sensitivity.
- To Differentiate in Crowded Markets: A unique and valuable loyalty program can be a significant competitive advantage, especially when price and product parity are common.
Successful Implementation Examples:
- Starbucks Rewards: A benchmark example integrating mobile pre-ordering, payment, points accrual (Stars), personalized offers, and tiered benefits seamlessly across its app and physical stores. Stars are earned and redeemed fluidly regardless of the purchase point.
- Sephora’s Beauty Insider: Connects online browsing/purchase history with in-store experiences. Members receive personalized product recommendations, birthday gifts, points redeemable for products or experiences, and access to tiered benefits (Insider, VIB, Rouge) with increasing exclusivity, all tracked via a single account.
- Nike Membership: Goes beyond transactions, linking activity within the Nike Training Club or Nike Run Club apps with member-exclusive product drops, early access, in-store benefits, expert advice, and personalized content, creating a holistic brand ecosystem.
- Marriott Bonvoy: Integrates experiences across its vast portfolio of hotel brands. Members use the app for mobile check-in, mobile keys, requesting amenities, and tracking points/status earned through stays, dining, or co-branded credit cards, redeemable globally.
Actionable Tips for Brand & Marketing Directors:
- Prioritize Experiential Value Over Pure Discounts: While discounts have a place, focus on creating unique experiences, exclusive access, early releases, and personalized recognition that competitors can’t easily replicate. Think emotional connection, not just transactional savings.
- Design a Seamless Enrollment and Redemption Process: Make it incredibly easy for customers to sign up and redeem rewards across all touchpoints. Remove friction – integrate with mobile wallets, enable easy look-up at POS, ensure website and app integration is flawless.
- Leverage Loyalty Data for Cross-Channel Personalization: Use the rich first-party data gathered to personalize email marketing, app notifications, website experiences, and even in-store interactions. Tailor offers and content based on past behavior and preferences.
- Implement ‘Surprise and Delight’ Moments: Use unexpected rewards or recognition based on loyalty milestones, birthdays, or specific behaviors to create memorable positive experiences that strengthen the emotional connection.
- Continuously Evolve Program Benefits: Regularly review and refresh program offerings based on customer feedback, data analysis, and market trends to maintain engagement and prevent the program from becoming stale.
Pros:
- Significantly increases customer lifetime value and retention rates.
- Provides a rich source of consented, cross-channel first-party data.
- Encourages customers to engage with the brand across multiple channels.
- Helps build deeper emotional connections beyond simple transactions.
- Offers a powerful way to differentiate the brand in competitive markets.
Cons:
- Can require significant investment in technology (e.g., CDP, loyalty platform) and ongoing maintenance.
- Creating truly unique and compelling benefits that stand out can be challenging.
- Risk of reward devaluation or “points inflation” if not managed carefully.
- Complexity in ensuring consistent implementation and recognition across all touchpoints, especially with franchise models or disparate legacy systems.
- May primarily attract discount-seeking customers if not carefully structured around value beyond price.
In summary, implementing an Integrated Loyalty Program is a strategic imperative for brands serious about excelling in omnichannel marketing strategies. It’s an investment in understanding, recognizing, and valuing customers consistently, wherever they choose to engage, ultimately driving sustainable growth and brand advocacy.
5. Buy Online, Pickup In-Store (BOPIS) and Omnichannel Fulfillment
At the heart of modern customer convenience lies the powerful fusion of digital browsing and physical acquisition, embodied by Buy Online, Pickup In-Store (BOPIS) and broader omnichannel fulfillment strategies. This approach represents a critical component of effective omnichannel marketing strategies, directly addressing the customer’s desire for flexibility and speed by seamlessly connecting the e-commerce experience with the immediacy and infrastructure of brick-and-mortar locations. It transforms physical stores from simple points of sale into dynamic hubs for fulfillment, customer service, and brand engagement.
How It Works:
The process typically begins with a customer browsing a retailer’s website or app. Key to this stage is real-time stock visibility, allowing the customer to see if an item is available for pickup at a nearby store. After adding items to their cart, the customer selects the BOPIS (or curbside pickup, ship-from-store, etc.) option at checkout and chooses their preferred store location. Behind the scenes, a unified inventory management system routes the order to the selected store. Store staff receive the order, pick the items from store inventory, stage them in a designated area, and notify the customer (often via email or SMS) when the order is ready. The customer then travels to the store, identifies themselves (often facilitated by geolocation services for curbside arrival notifications), and receives their purchase quickly, bypassing traditional checkout lines.
Why It Deserves a Place on This List:
BOPIS and related omnichannel fulfillment options are no longer niche offerings; they are foundational expectations for many consumers. This strategy directly tackles the core challenge of omnichannel marketing strategies: creating a unified, frictionless experience across all touchpoints. It leverages existing physical assets (stores and staff) to enhance the digital offering, providing a distinct competitive advantage over pure-play e-commerce retailers who lack a physical footprint for immediate pickup or returns. It fundamentally reshapes the role of the physical store, integrating it deeply into the digital customer journey. For industries like beverages or spirits where immediacy can be a key purchase driver (e.g., picking up drinks for an impromptu gathering), BOPIS offers significant value.
Specific Features and Benefits:
- Unified Inventory Management: Provides a single view of stock across warehouses, distribution centers, and individual stores. This minimizes “out-of-stock” disappointments online and allows fulfillment from the most efficient location.
- Real-time Stock Visibility: Empowers customers to confidently order for pickup, knowing the item is available locally. This reduces friction and abandoned carts.
- Multiple Fulfillment Options: Beyond standard BOPIS, this includes curbside pickup (even greater convenience), ship-from-store (faster local delivery leveraging store inventory), and locker pickups (secure, self-service). This caters to diverse customer preferences for speed, cost, and contact levels.
- Geolocation Services: For curbside, apps can notify staff of the customer’s imminent arrival, minimizing wait times and streamlining the handover process.
- Cross-sell/Upsell Opportunities: The pickup interaction, whether in-store or curbside, presents a valuable moment for trained staff to suggest complementary items, highlight promotions, or simply reinforce brand value through positive interaction.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Target: Their “Drive Up” service saw explosive growth (reporting 734% during the pandemic peak) and remains a cornerstone of their strategy, known for its speed and efficiency, demonstrating excellent integration of app notifications and dedicated staff.
- Best Buy: Successfully pivoted many locations to function heavily as fulfillment hubs, dedicating significant store space for processing online orders and implementing efficient ship-from-store logistics.
- Walmart: Offers a wide array of options, from in-store pickup towers for general merchandise to dedicated grocery pickup bays and expanding delivery services, showcasing scale and adaptability.
- Home Depot: Effectively uses designated pickup areas and secure lockers within stores, catering to both consumers and professional contractors needing quick access to online orders.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Dedicate Physical Space: Clearly designate areas within the store solely for staging and picking up online orders. This minimizes disruption to regular shoppers and streamlines the process for staff and BOPIS customers.
- Invest in Staff Training: Fulfillment staff need thorough training on the order management system (OMS), picking accuracy, packing standards, customer service protocols for pickup interactions, and handling exceptions or returns.
- Prioritize Clear Communication: Utilize automated emails, SMS alerts, and in-app notifications to keep customers informed about order status (received, processing, ready for pickup) and provide clear instructions on the pickup procedure (where to go, what to bring).
- Implement Robust Technology: An integrated Order Management System (OMS) that connects the e-commerce platform, inventory systems, and Point-of-Sale (POS) is crucial for real-time visibility and operational efficiency.
- Leverage the Pickup Moment: Train staff to view the pickup not just as a transaction, but as an engagement opportunity. Equip them with relevant (but not intrusive) cross-selling suggestions based on the order or customer history, or simply focus on providing a fast, friendly, and positive brand interaction.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Directly meets heightened customer expectations for convenience and choice; significantly reduces last-mile delivery costs; increases foot traffic, potentially leading to impulse purchases; makes better use of existing retail store investments; creates a strong competitive differentiator against online-only rivals.
- Cons: Requires substantial changes to in-store operations and workflows; accurate, real-time inventory management across all channels is complex and critical; necessitates significant staff training and potential reallocation; poor execution (long waits, inaccurate orders) can severely damage customer perception; integrating disparate technology systems (e-commerce, POS, inventory, OMS) can be challenging and costly.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Brands with existing physical retail locations should strongly consider implementing BOPIS and omnichannel fulfillment strategies. Use this approach when your goals include:
- Increasing customer convenience and providing flexible shopping options.
- Reducing shipping costs and improving fulfillment speed (especially for local customers).
- Driving incremental traffic to physical stores.
- Maximizing the utility of existing store infrastructure and inventory.
- Competing effectively with both e-commerce giants and other brick-and-mortar retailers offering similar services.
Implementing BOPIS is a significant undertaking requiring commitment across operations, technology, and marketing, but when executed well, it becomes a powerful engine for customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and sales growth within a comprehensive omnichannel marketing strategy.
6. Unified Messaging and Brand Voice
What it is: Unified Messaging and Brand Voice is a cornerstone of effective omnichannel marketing strategies. It revolves around meticulously maintaining a consistent brand identity, encompassing tone of voice, messaging hierarchy, and visual elements, across every single customer touchpoint. However, it’s not about rigid uniformity; it crucially involves adapting this core identity to suit the unique context, constraints, and audience expectations of each specific channel. Whether a customer interacts with your brand via a social media post, an email newsletter, a chatbot, an in-store display, a customer service call, or product packaging, the experience should feel coherent and recognizably yours.
How it Works: This strategy requires a deliberate and structured approach, underpinned by several key features:
- Centralized Content Strategy and Governance: A master plan dictates core messages, campaign themes, and overall narrative arcs. A governance structure ensures adherence to guidelines.
- Consistent Visual Identity System: Logos, color palettes, typography, imagery style, and layout principles are standardized and applied across all platforms, ensuring visual recognition.
- Tonal Framework: Defines the brand’s personality (e.g., playful, authoritative, empathetic) and provides guidelines on how this tone should modulate in different situations (e.g., marketing vs. support) and on different channels (e.g., concise and informal on Twitter vs. more detailed and formal in a whitepaper).
- Message Architecture: Outlines the hierarchy of key messages for specific campaigns or initiatives, ensuring the most important points are prioritized consistently across channels.
- Channel-Specific Content Adaptation Guidelines: Crucial “playbooks” that explain how to translate the core brand voice and messaging for the nuances of each platform (e.g., character limits, visual formats, user behavior).
- Centralized Digital Asset Management (DAM): A system for storing, organizing, and distributing approved brand assets (logos, images, videos, copy blocks), ensuring teams use the correct, up-to-date materials.
Why it Deserves its Place: In an omnichannel world, customers don’t see channels; they see a single brand. Inconsistency fractures this perception. A unified voice acts as the essential connective tissue linking disparate touchpoints into a seamless journey. It moves beyond simply coordinating channels to actively shaping a singular, cohesive brand perception in the customer’s mind, which is fundamental to the success of any omnichannel marketing strategies. For sectors like beverage, retail, and spirits, where brand perception and emotional connection are paramount, this consistency is non-negotiable for building lasting loyalty.
Benefits (Pros):
- Strengthens Brand Recognition and Recall: Consistent cues make the brand instantly identifiable and memorable.
- Builds Trust and Credibility: Reliability in messaging and visuals fosters customer confidence.
- Increases Campaign Effectiveness: Reinforcing key messages across multiple channels boosts overall impact and ROI.
- Improves Operational Efficiency: Clear guidelines and shared assets streamline content creation and reduce duplicated effort.
- Enhances Scalability: A defined framework makes it easier to expand marketing efforts to new channels or markets consistently.
Challenges (Cons):
- Maintaining Consistency: Can be difficult, especially with large or decentralized teams (e.g., global franchises, multiple agencies).
- Coordination Complexity: Requires significant collaboration between departments (Marketing, Sales, Product, Customer Service, Retail Operations).
- Risk of Formulaic Messaging: Over-strict adherence can stifle creativity and lead to messaging that feels bland or poorly optimized for a specific channel’s context. Finding the balance between consistency and adaptation is key.
- Slower Content Production: Governance and approval processes can sometimes introduce delays, challenging the need for agility in channels like social media.
- Cultural Adaptation: Global brands face the added challenge of adapting the core voice and visuals appropriately for different cultural contexts and languages while maintaining global identity.
Successful Examples:
- Apple: Masterfully executes a minimalist, premium aesthetic and a direct, user-focused tone across its meticulously designed retail stores, product packaging, website, software interfaces, and advertising campaigns. The experience feels seamless and quintessentially Apple at every touchpoint.
- Coca-Cola: Employs rigorous brand guidelines globally, ensuring the iconic red, dynamic ribbon, and themes of happiness and togetherness are instantly recognizable, whether on a billboard in Tokyo, a social media campaign in Brazil, or a vending machine in Chicago. Local adaptations exist, but the core brand DNA remains consistent.
- Disney: Adapts its signature “magical,” family-friendly, and storytelling-centric voice across an incredibly diverse range of touchpoints – from theme park interactions and movie trailers to streaming service interfaces (like Disney+), merchandise, and customer support – always feeling appropriately Disney for the context.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
- When: This approach is essential for virtually any brand engaging in omnichannel marketing, but it becomes critically important when:
- Operating across numerous customer touchpoints (digital, physical, support).
- Brand perception, trust, and emotional connection are key purchase drivers (highly relevant for beverage, retail, spirits, luxury, and lifestyle brands).
- Managing complex customer journeys with multiple interactions before conversion.
- Aiming to build long-term brand equity and customer loyalty rather than just short-term sales.
- Scaling marketing operations across new regions or channels.
- Why: Use this strategy to eliminate jarring inconsistencies that erode trust and confuse customers. It ensures that every interaction reinforces the brand’s core values and identity, creating a stronger, more resilient, and more valuable brand presence in the market. It transforms disparate marketing activities into a unified brand conversation.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Develop Comprehensive Brand Guidelines: Create a detailed yet easily accessible “brand bible” covering voice, tone, visual identity, and messaging principles.
- Create Channel Playbooks: Provide specific, practical guidance on how to adapt the core brand identity for key channels (e.g., Instagram best practices, email signature rules, in-store signage templates).
- Implement Regular Cross-Channel Audits: Periodically review content across all touchpoints to identify and correct inconsistencies.
- Use Shared Tools and Workflows: Employ shared content calendars, project management tools, and DAM systems with clear approval processes to foster collaboration and consistency.
- Train All Customer-Facing Staff: Ensure everyone who interacts with customers (marketing, sales, support, retail staff) understands and embodies the brand voice principles.
- Establish a Central Brand Governance Team or Process: Designate individuals or a committee responsible for overseeing brand consistency, updating guidelines, and resolving ambiguities.
By prioritizing Unified Messaging and Brand Voice, companies can ensure their omnichannel marketing strategies deliver a powerful, cohesive, and trustworthy brand experience that resonates deeply with customers.
7. Cross-Channel Attribution and Analytics
In today’s fragmented customer journey, understanding what truly drives conversions and engagement is paramount. Simply executing campaigns across multiple channels isn’t enough; effective omnichannel marketing strategies demand insight into how these channels work together. This is where Cross-Channel Attribution and Analytics becomes indispensable.
What is Cross-Channel Attribution and Analytics?
At its core, Cross-Channel Attribution and Analytics is the strategic practice of tracking, analyzing, and assigning value to customer interactions across the myriad touchpoints they encounter before reaching a desired outcome (like a purchase, sign-up, or app download). It moves beyond simplistic “last-click” thinking, which often overvalues bottom-of-funnel activities, to provide a more holistic and accurate picture of marketing performance. By employing sophisticated modeling techniques, businesses can understand the relative contribution of each channel – from initial awareness generated by a social media ad to a final decision influenced by an email promotion – in guiding the customer along their path.
How Does It Work?
Implementing this strategy involves several key components:
- Data Collection: Meticulously tracking user interactions across all relevant online and offline channels. This requires robust tagging, consistent identifiers (where possible), and integrating data from various platforms (CRM, website analytics, ad platforms, POS systems).
- Unified View: Stitching together data points to create a unified profile of individual customer journeys, even as they switch devices or move between online research and offline purchase. Features like unified cross-device tracking and online-to-offline conversion measurement are crucial here.
- Attribution Modeling: Applying mathematical models to distribute credit for conversions among the various touchpoints. This ranges from basic models (First-Click, Last-Click, Linear) to advanced multi-touch attribution models (Time Decay, U-Shaped, Data-Driven) that attempt to assign credit more accurately based on channel position and influence. Marketing mix modeling (MMM) often complements this by analyzing aggregate data over longer periods to assess broader channel impact, while incrementality testing helps isolate the true causal effect of specific marketing actions.
- Analysis & Insight: Using the outputs of these models to perform customer path analysis, identify friction points, understand high-performing sequences, and generate actionable insights for optimization.
Why This Strategy is Crucial for Omnichannel Success
Cross-Channel Attribution and Analytics deserves its place in this list because it provides the necessary intelligence to manage and optimize the complexity inherent in omnichannel marketing. Without it, marketers risk:
- Misallocating budgets based on incomplete or misleading data.
- Failing to understand the synergistic effects between channels.
- Under-investing in upper-funnel activities that build awareness and consideration but don’t get last-click credit.
- Operating in channel-specific silos without a shared understanding of overall performance.
Essentially, it transforms omnichannel marketing strategies from a collection of disparate activities into a cohesive, measurable, and optimizable system.
Benefits and Features:
- Enhanced Visibility: Gain a true understanding of which channels and campaigns genuinely drive results.
- Efficient Budget Allocation: Shift marketing spend towards the most effective touchpoints and journeys, maximizing ROI.
- Journey Optimization: Identify and replicate high-performing customer paths while fixing bottlenecks in others.
- Breaking Down Silos: Foster collaboration by providing shared metrics and a common understanding of cross-channel impact.
- Justifying Investment: Prove the value of seemingly less direct channels (e.g., content marketing, social media engagement) that play crucial roles earlier in the funnel.
Potential Challenges:
- Technical Complexity: Implementation requires significant technical expertise and robust data infrastructure.
- Data Privacy: Evolving regulations (like GDPR, CCPA) and browser changes (cookie restrictions) make tracking more challenging.
- Imperfect Models: No single attribution model is universally perfect; each has biases and limitations.
- Resource Intensive: Often requires dedicated data science or analytics resources.
- Organizational Resistance: Channel-specific teams may resist findings that diminish their perceived contribution.
Real-World Examples:
- Airbnb: Developed sophisticated, custom attribution models to better understand the interplay between various online searches, ad exposures, email interactions, and even offline factors influencing bookings, allowing for smarter marketing investment globally.
- Macy’s: Implemented technology to connect digital ad exposure data with in-store visit tracking, enabling them to measure the offline impact of their online advertising campaigns and optimize spend accordingly.
- Procter & Gamble (P&G): Famously analyzed their digital advertising effectiveness using advanced attribution insights, leading to a significant reallocation of approximately $200 million away from digital ads deemed ineffective or lacking transparency, focusing instead on channels with proven reach and impact.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Start Simple: Begin with basic attribution models (e.g., linear or time decay) and gradually evolve towards more complex data-driven or custom models as your capabilities mature.
- Focus on Incrementality: Don’t chase perfect attribution. Instead, focus on making incremental improvements based on the insights you gain. Use lift testing to validate causal impact.
- Combine Methodologies: Use a blend of approaches (e.g., multi-touch attribution for granular path analysis, marketing mix modeling for strategic budget allocation) for a more holistic view.
- Test and Validate: Regularly test your models against real-world outcomes and validate their predictive power.
- Consistent KPIs: Establish and use consistent Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) across channels wherever possible to facilitate comparison.
- Prioritize Tracking: Ensure proper tagging and tracking mechanisms are implemented correctly from the beginning across all relevant customer touchpoints.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Employ Cross-Channel Attribution and Analytics when your customer journeys span multiple touchpoints (online and/or offline), when you make significant investments across various marketing channels, and when you need to justify marketing spend and optimize budget allocation based on demonstrable contribution to business outcomes. It’s particularly vital for businesses aiming to deliver seamless, personalized omnichannel marketing strategies and move beyond guesswork to data-driven decision-making. While challenging, the insights gained are fundamental to achieving true omnichannel mastery. Leading platforms and consultancies like Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, Nielsen, Neustar, and Marketing Evolution offer tools and expertise in this domain.
Omnichannel Strategy Comparison Matrix
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Journey Mapping | Medium to High: requires cross-team collaboration and frequent updates | Moderate to High: needs data, tools, and expertise | Holistic customer insights, gap identification, improved experience | Customer experience optimization, channel integration | Comprehensive view of customer interactions, prioritizes marketing efforts |
| Unified Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) | High: technical integration with legacy systems, ongoing maintenance | High: technical, IT, and marketing collaboration | Single customer view, better targeting and personalization | Data unification, omnichannel marketing, compliance management | Eliminates data silos, boosts personalization, improves ROI |
| Personalized Content Orchestration | High: complex AI-driven content generation and multi-channel management | High: strong content creation and data quality demands | Increased engagement and conversions through tailored messaging | Driving engagement with dynamic, journey-based content | Scales personalization, reduces message fatigue, supports customer progression |
| Integrated Loyalty Programs | Medium to High: involves program design, tech integration, and maintenance | Moderate to High: marketing, IT, and rewards management | Increased customer retention, lifetime value, multichannel engagement | Customer retention, emotional brand connection | Provides first-party data, encourages engagement, differentiates brand |
| BOPIS and Omnichannel Fulfillment | High: operational overhaul in stores, inventory, and tech integration | High: inventory, POS, staff training, and notification systems | Customer convenience, reduced shipping costs, increased store traffic | Retailers combining physical and digital sales channels | Flexible fulfillment, leverages store assets, competitive advantage |
| Unified Messaging and Brand Voice | Medium: governance and coordination across decentralized teams | Moderate: content strategy, training, and brand management | Consistent brand identity, increased trust, scalable marketing | Maintaining coherence in multi-channel brand communication | Strengthens recognition, builds trust, improves efficiency |
| Cross-Channel Attribution and Analytics | High: advanced modeling, data integration, significant data science | High: data infrastructure, analytics expertise, compliance monitoring | Clear channel impact insights, optimized marketing spend | Marketing performance measurement and budget optimization | Enables efficient budget allocation, breaks down silos, justifies spend |
Bringing Your Omnichannel Vision to Life
We’ve explored the essential pillars of modern customer engagement: from deeply understanding the customer journey and leveraging Unified Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) to orchestrating personalized content, integrating loyalty programs, and mastering omnichannel fulfillment like BOPIS. We’ve also highlighted the importance of a unified brand voice and robust cross-channel attribution to measure success effectively.
The core takeaway is clear: successful omnichannel marketing strategies are built on seamless integration and a relentless focus on the customer experience. It’s about moving beyond siloed channels to create a single, cohesive ecosystem where your brand interacts consistently and meaningfully with consumers, wherever they choose to engage. For Brand Directors, Marketing Directors, and CMOs, particularly in competitive sectors like beverage, spirits, and retail, mastering this approach is no longer a luxury, but a necessity for building loyalty and driving growth.
Your actionable next steps should involve auditing your current capabilities across these seven key areas. Identify the gaps in your customer journey mapping, evaluate your data infrastructure, assess your personalization potential, and critically examine your fulfillment and messaging consistency. Prioritize investing in the technology and cross-functional collaboration needed to bridge these gaps.
Implementing comprehensive omnichannel marketing strategies requires commitment, strategic planning, and often, the right expertise. However, the rewards – deeper customer loyalty, increased lifetime value, higher conversion rates, and a stronger competitive advantage – are invaluable. It’s about building a resilient brand that not only meets customer expectations but consistently exceeds them across every touchpoint. Embrace the challenge, focus on integration, and watch your customer relationships flourish.
Ready to elevate your retail presence with seamless omnichannel marketing strategies tailored for CPG, food, and beverage brands? Theory House leverages deep shopper insights and integrated expertise to turn consumer passion into purchase, online and in-store. Discover how they can help bring your vision to life at Theory House.




